CNC Plastic Machining Services – Custom Machined Plastic Parts Manufacturer in China
As a China-leading CNC parts manufacturer, Junying is specialized in fabricating various custom-machined plastic parts using CNC equipment and technologies, our CNC plastic machining services provide the most efficient and economical solutions for rapid prototyping and mass production runs. Extensive experience and skilled experts enable us to work with complex shapes and rare materials, and produce customized plastic CNC machining parts according to customers’ needs. We’ll select high-quality and high-performance plastic materials, whether you want ABS, PS, PC, Nylon, PEEK, PA, POM, or other types to make the products. Junying is a CE and ISO 9001 certificated CNC manufacturer and is able to offer high-precision CNC machined plastic parts with tight tolerances and premium properties required in critical industries.
Why Choose Junying Plastic CNC Machining Services?
-

A wide selection of high-performance engineering plastic materials in stock
-
State-of-the-art machining, manufacturing, and measurement facilities
-

Complete quality management system and professional inspection before shipment
-
Premium quality CNC plastic parts with custom specifications and high accuracy
-

Strong capacity for CNC programming, 5-axis machining, and precision production

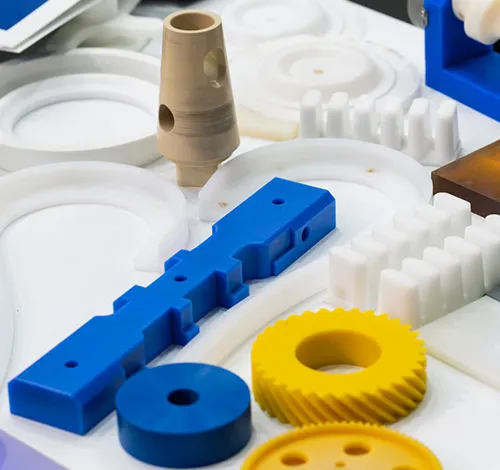
CNC Plastic Machining Materials at Junying
- CNC Machining ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- CNC Machining POM (Polyoxymethylene)/Acetal/Delrin
- CNC Machining PE (Polyethylene)/HDPE/LDPE/UHMW-PE
- CNC Machining PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate)/Acrylic
- CNC Machining PA (Polyamide)/Nylon
- CNC Machining PC (Polycarbonate)
- CNC Machining PEEK (Polyetheretherketone)
- CNC Machining PTFE ( (Polytetrafluoroethylene)/Teflon
- CNC Machining PS (Polystyrene)
- CNC Machining PP (Polypropylene)
- CNC Machining PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
- CNC Machining Garolite G-10
CNC Plastic Machining Services & More Capabilities at Junying

Plastic CNC Fabrication

Plastic CNC Turning

5-Axis Plastic Machining

Full 3D CMM Measurement

Laser Scan and Reverse Engineer
Common Plastic Manufacturing & Fabrication Techniques

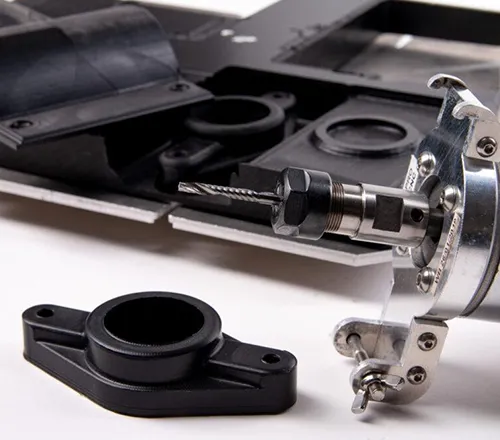
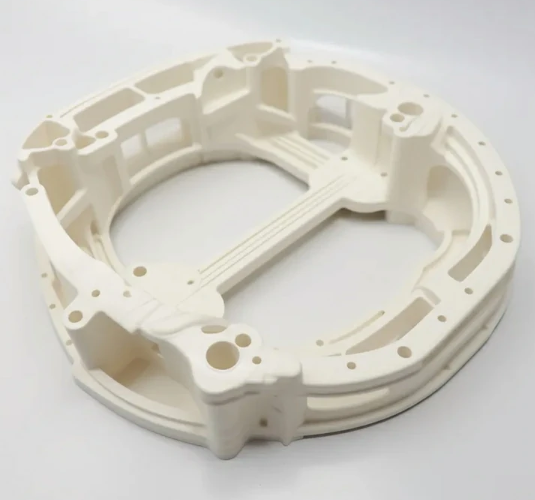
A machining process that involves removing material from a plastic workpiece using a rotating cutting tool. The workpiece is secured to a work-holding device such as a vise, clamp, or fixture. The cutting tool is brought into contact with the workpiece and rotated at high speeds. As the cutting tool rotates, it removes material from the workpiece, producing the CNC milled plastic parts with desired shape and size.
Sizes: 1-14,000 mm (length), 1-2,500 mm (width), 1-730mm (thickness), up to 3,500 mm (ø)

A machining process used to shape a plastic workpiece on a lathe. Turning involves rotating the plastic workpiece on a lathe while a cutting tool removes material from the workpiece to create the desired shape and size. The cutting tool can be a single-point cutting tool, a parting tool, a boring tool, or a grooving tool.
Sizes: 0.5-2,000 mm (ø), max.2,300 mm (length)

A process used to produce continuous lengths of plastic profiles with a constant cross-section. The process involves feeding plastic material (usually in the form of pellets or powder) into an extruder, which melts and mixes the material and then forces it through a die to form the desired shape.
Sizes: ranging from 0.25” wide and .0005” thick to 12” wide and 4” thick

A manufacturing process used to form thin sheets of plastic into three-dimensional shapes by heating and molding the plastic material. During the process, the plastic sheet is heated to a specific temperature until it becomes pliable, and then shaping it into the desired form using a mold.
Sizes: max. 1,600 mm (length), max. 1,200 mm (width), max. 30 mm (panel thickness)

A process of creating three-dimensional plastic objects by adding layer upon layer of plastic material. The process involves using a computer-aided design (CAD) file to guide the printing process and create the desired object. Typical 3D printing technologies include FDM, SLA, SLS, etc.
Sizes: varies based on the technology and material, for example, 750 x 550 x 550 mm of SLS

Also known as Urethane casting or Polyurethane casting, a process that uses silicone molds to make plastic and rubber components by pouring liquid plastic material into the mold under a vacuum.
Sizes: min. 0.75 mm (mold wall thickness), max. 1900 x 900 x 750 mm.
Surface Finishing & Treatment Processes for Plastic Parts
A variety of surface finishing and treatment processes can also be performed on plastic products, sometimes the surface finish can even be comparable to metals.
| Painting | Applying a layer of paint or coating onto the plastic surface, which adheres to the plastic and forms a protective layer. |
| In-mold Decoration (IMD) | Putting the printed film into the mold in different types to obtain a molded part with printed texture after the plastic injection molding. |
| Plating | Immersing the plastic part into an electrolytic bath containing metal ions, and then applying an electrical current to deposit the metal onto the surface of the plastic. |
| Printing | Printing the required patterns on the surface of plastic parts through different methods, including pad printing, screen printing, and water transfer printing. |
| Laser Engraving | Also known as laser marking, label or mark the plastic components using a laser machine, to type of pattern on the surface of the product. |
| Thin Film Deposition | A process by which very thin layers are deposited on a substrate |
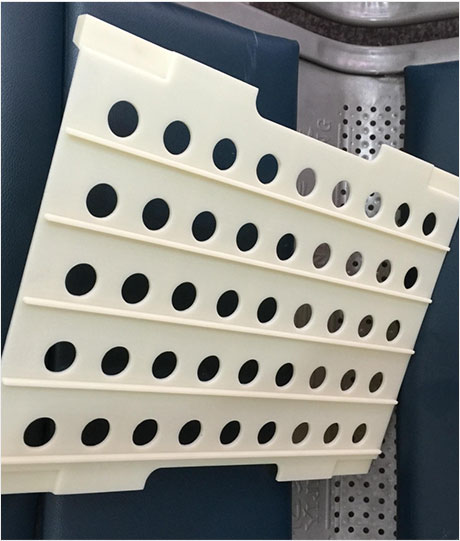
Plastic CNC Machining Parts Required
Contact UsCommon CNC Machining Plastic Types, Properties and Uses
In plastic CNC machining, the final product is made by removing excess materials from a plastic block using digital computer control machines. A wide selection of plastic and polymers can be machined on CNC equipment, check out some of the common CNC machining plastics, with their characteristics and applications.

ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a widely used engineering plastic, recognized for its versatility and well-balanced set of properties. It typically appears as light yellow or milky white granular resin with an amorphous molecular structure. This plastic is composed of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, each contributing to its distinctive characteristics.
ABS Plastic Properties:
- Strong resistance to impact, suitable for demanding and tough environments
- Capable of withstanding both high and low temperature conditions
- Demonstrates chemical resistance along with effective electrical insulating properties
- Maintains dimensional stability and can be machined with ease
- Smooth surface finish that readily accepts painting, electroplating and welding
ABS Plastic Applications:
Automotive manufacturing for dashboards and trims, electronics for device housings, machinery components, parts for textile equipment, construction materials, and precision instruments like meters.
Polyamide (PA or Nylon)
Polyamide, commonly known as Nylon, encompasses types like Nylon 6 and Nylon 66, which are highly valued for their mechanical robustness and durability. Nylon 6 is noted for exceptional toughness, stiffness, and wear resistance, whereas Nylon 66 provides improved heat resistance and mechanical strength, albeit with somewhat reduced impact absorption.
Nylon Plastic Properties:
- High mechanical strength and rigidity
- Excellent resistance to wear, abrasion, and mechanical shock
- Functions well as an electrical insulator
- Resists various chemicals
- Nylon 66 specifically features superior heat resistance and creep resistance
Nylon Plastic Applications:
Nylon machined parts are widely found in automotive components, instrument housings, and mechanical structures requiring robust impact resistance and durability. Nylon 66 is particularly favored for automatic lathe machining due to its enhanced mechanical properties.

POM (Polyoxymethylene/Delrin/Acetal)
POM is a crystalline engineering plastic renowned for its toughness and elasticity. It exhibits excellent resistance to creep and retains its shape under mechanical stress. The material is characterized by a very low coefficient of friction, and suitable for moving parts.
POM Plastic Properties:
- High impact strength, even in low-temperature environments
- Outstanding dimensional stability
- Low friction combined with excellent wear resistance
- Resists high temperatures and chemical exposure effectively
- High crystallinity leads to noticeable shrinkage during processing
POM Plastic Applications:
POM is commonly applied in the manufacture of precision gears and bearings. Additional uses include pipeline valves and pump housings, automotive components such as door handles and mirrors, household appliances like hairdryers and washing machines, as well as precision instruments including clocks and cameras.
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate/Acrylic)
PMMA, also known as acrylic or plexiglass, is a transparent thermoplastic with excellent optical clarity. It has a long history of development and is well known for ease of processing and attractive visual qualities.
PMMA Plastic Properties:
- High transparency comparable to glass
- Good chemical stability and weather resistance
- Can be easily dyed and shaped into different forms
PMMA Plastic Applications:
This plastic is frequently used in the production of advertising light boxes, nameplates, display cases, and other decorative or transparent components. It also finds use in automotive lamps, tubes, glazing, and transparent valves, often serving as a replacement for glass.


PC (Polycarbonate)
Polycarbonate is a high-performance polymer containing carbonate groups within its molecular chain. It is a versatile material, prized for its combination of strength and clarity across diverse industries.
PC Plastic Properties:
- Excellent impact resistance and toughness
- Good heat resistance and dimensional stability
- Outstanding electrical insulating properties
- Combines transparency with structural strength
PC Plastic Applications:
PC is deployed in glass assembly, automotive parts, electronics and electrical components, optical discs, packaging materials, office equipment, medical devices, protective gear, and recreational products.PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
PEEK is a specialty engineering plastic celebrated for its outstanding performance in extreme conditions. It resists high temperatures and combines superior mechanical and chemical resistance.
PEEK Plastic Properties:
- Can operate continuously at temperatures up to 260°C
- Exceptional mechanical strength and wear resistance
- Self-lubricating properties that reduce friction
- Resists chemicals, flames, peeling, and radiation
- Maintains durability when exposed to strong acids and harsh environments
PEEK Plastic Applications:
PEEK is utilized in highly demanding fields including aerospace, nuclear engineering, and high-end machinery, where material reliability under severe conditions is essential.


PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene/Teflon)
PTFE is a synthetic fluoropolymer in which fluorine atoms substitute all hydrogen atoms in polyethylene, creating unique chemical and physical properties.
PTFE Plastic Properties:
- Resistant to acids, alkalis, and most organic solvents
- Nearly insoluble in all solvents
- Capable of withstanding very high temperatures
- Possesses the lowest coefficient of friction among all materials (excellent lubricant)
- Chemically inert and highly non-reactive
PTFE Plastic Applications:
PTFE is widely used as a non-stick coating for cookware and pipes, as a lubricant in machinery, and as lining material for tubes and fittings exposed to aggressive chemicals. It is also common in seals such as O-rings and gaskets, medical equipment, insulation, and chemical processing devices.
PE (Polyethylene)
Polyethylene is an extensively used thermoplastic available in various grades, including high-density (HDPE), low-density (LDPE), and linear low-density (LLDPE). It is favored for its excellent machinability and versatility across many industries.
PE Plastic Properties:
- Easily machined and shaped into complex parts
- Cost-effective with good mechanical strength
- Strong resistance to chemicals and moisture
- Different density variants provide a range of rigidity and flexibility
PE Plastic Applications:
HDPE is commonly used for water pipes, chemical containers, and packaging. LDPE is popular for plastic bags and films. Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMW-PE) is chosen for abrasion-resistant parts and specialized medical applications.


PP (Polypropylene)
Polypropylene is a lightweight yet durable thermoplastic exhibiting excellent chemical resistance and the ability to withstand relatively high temperatures.
PP Plastic Properties:
- Low density combined with high strength
- Resistant to many chemical agents
- High melting point
- Accommodate detailed and complex shapes
PP Plastic Applications:
PP is widely utilized in automotive components, packaging materials, electrical parts such as switches and sockets, and consumer goods that demand chemical resistance and durability.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Polyvinyl Chloride, commonly known as PVC or vinyl, is a high-strength and cost-effective thermoplastic material that ranks as the world’s third most produced synthetic plastic polymer after polyethylene and polypropylene. PVC appears as a white, brittle solid, usually available in powder or granule form. Over time, it has replaced traditional building materials such as wood, metal, concrete, rubber, and ceramics in many applications because of its lightweight nature, robustness, low cost, and ease of processing. Common types of forms PVC include rigid PVC and flexible PVC.
PVC Plastic Properties:
- Excellent dielectric material that provides good insulation in electrical and electronic applications
- Resists weathering, chemical degradation, corrosion, mechanical shock, and abrasion
- Flame retardancy and self-extinguishment with a high chlorine content
- Tough, abrasion-resistant, and lightweight, combining strength with ease of handling
- Resistant to a wide range of inorganic chemicals, including diluted acids, alkalis, and aliphatic hydrocarbons
PVC Plastic Applications:
Window frames, pipes, house siding, roofing, and ports in construction; Car seat backs, roof linings, window seals, wiring insulation, decorative trims in automotive and transport; Oxygen tents, blood transfusion bags and tubing, drips in medical, packaging bottles, electronics, etc.


PS (Polystyrene)
Polystyrene (PS) is a polymer that can exist as either a thermoplastic to be melted and reshaped multiple times, or a thermoset, which cannot be remelted after curing. The thermoplastic form is predominantly used in injection molding and CNC machining due to its recyclability and ease of fabrication. The primary types of polystyrene include General-Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS), High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) and Expanded Polystyrene (EPS).
PS Plastic Properties:
- Non-toxic, odorless, and lightweight
- High impact strength and good dimensional stability
- Excellent electrical insulation properties
- Poor chemical resistance, which limits its use with certain solvents but contributes to its long-lasting nature in natural environments
- Brittle by nature, particularly in its unmodified state
- Transparent due to the amorphous arrangement of styrene molecules
- Glass transition temperature around 100°C, where the polymer softens before melting
PS Plastic Applications:
Petri dishes, test tubes, and other laboratory equipment in medical; Food containers, rigid silverware, and protective films in packaging; Display stands, toys, and protective laminates for consumers; Insulation foams, yogurt containers, automotive and electronics components.
Both CNC machining and laser cutting are popular techniques for cutting plastics, and each of the processes has its own advantages and disadvantages. The better option is determined by the specific requirements.
CNC machines are known for their accuracy and precision in cutting. They can cut plastics of various thicknesses, sizes, and shapes. CNC machines can also perform different types of cuts, including drilling, routing, and engraving. Plastic CNC machining can be used for both 2D and 3D cutting and can work with a wide range of materials. If precision and accuracy are the most important factors, CNC machining may be the better choice.
Laser cutters are very precise and accurate as well, and are particularly good at cutting thin sheets of plastic. Laser cutters can produce intricate designs with a high level of detail, and can cut through thick plastics quickly and efficiently. They also leave a clean, polished edge on the cut surface, which can be an advantage in some applications. If intricate designs and clean edges are needed, a laser cutter may be the better option. As a plastic CNC machining China supplier, Junying also provides on-demand sheet metal fabrication and various cutting techniques.
There is a wide range of cutting speeds for plastics according to the type of material, thickness, cutting method, equipment, and more factors. If you are using a CNC machine to cut plastic, the cutting speed can range from a few inches per minute (IPM) for thicker materials like acrylic or polycarbonate to several hundred IPM for thinner materials like PVC or HDPE. As a general guideline, the cutting speed for plastic on a CNC machine can range from 50 IPM (1,270 mm/min) for thicker materials such as acrylic or polycarbonate to 500 IPM (12,700 mm/min) for thinner materials such as PVC or HDPE.
Generally, plastic CNC machining can range from a few dollars for simple parts to several hundred or even thousands of dollars for more complex and larger parts. Welcome to upload your drawing on CNCLATHING.COM to get a free online quote quickly. The cost of plastic CNC machining is affected by various factors.
– Material cost: The cost of the plastic material used for CNC machining can vary widely depending on the type, grade, and quantity needed.
– Machining time: The amount of time required to machine the part will affect the total cost. The longer the machining time, the higher the cost.
– Labor cost: The cost of the labor required to program and operate the CNC machine will also impact the overall cost.
– Tooling cost: The cost of the cutting tools used for CNC machining will be different because of the type, size, and the number of tools.
– Post-processing and finishing costs: Additional processes such as polishing, sanding, or coating may be required after machining, which can also increase the cost.
|
Plastic Type |
Machinability |
|
ABS |
Excellent |
|
PP (Polypropylene) |
Excellent |
| PE (HDPE & LDPE) | Excellent |
|
Acrylic (PMMA) |
Excellent |
|
POM (Acetal) |
Excellent |
| PS (Polystyrene) | Excellent |
| PTFE (Teflon) | Excellent |
|
Nylon (PA) |
Fair to Good |
|
PC (Polycarbonate) |
Fair to Good |
|
PEEK |
Fair |
|
PBT |
Fair |
|
PEI (Polyetherimide) |
Fair to Poor |
|
PET |
Good |
|
PVC |
Fair |
Yes, you can drill plastic, but it is important to recognize that a drill’s main purpose is to create holes rather than to cut or shape plastic like a saw or milling tool. A standard twist drill bit removes material by twisting, producing round holes rather than slots or profiles. Trying to use a drill bit as a milling cutter or slotting tool on plastic often leads to problems such as melted material, rough edges, and cracking. This happens because the rake angle of typical drill bits is too aggressive for thermoplastics, causing the cutting edge to dig in and grab the plastic. Friction generates heat that melts the plastic, which can then weld back onto the bit or workpiece. Plastics like acrylic, polystyrene, and PET are especially prone to cracking under the high thrust forces applied by a drill.
The best choice between plastic machining and 3D printing depends heavily on your specific project requirements, such as part complexity, volume, budget, mechanical properties, and lead times.
Opt for CNC machining when your plastic parts demand high mechanical strength, dimensional accuracy, tight tolerances, and excellent surface quality and are produced in medium to high volumes. It is especially suitable when using engineering plastics that require superior thermal and chemical resistance. CNC machining is also preferred for parts with simple to moderately complex geometries where cost efficiency and repeatability are critical.
3D printing is the better choice for rapid prototyping, low-volume production, and parts with complex or organic shapes that cannot be easily machined. It is ideal when fast turnaround and design flexibility outweigh the need for maximum strength or surface finish. Additionally, 3D printing is suitable for specialized materials unavailable in CNC machining or when tooling costs need to be minimized.


