HVOF Tungsten Carbide Coating Services Supplier – Tungsten Carbide Surface Finish
Junying Metal Manufacturing Co., Ltd., recognized as a leading provider of CNC machining services in China, also excels in the tungsten carbide coating surface finishing service. HVOF tungsten carbide coating is one of the most common surface treatments applied for steel workpieces. With advanced technology and a team of skilled engineers, Junying offers precision HVOF thermal spray tungsten carbide that enhances the durability and performance of various components. If you are seeking a reliable coating supplier, we’ll ensure the highest quality and strict industry standards. Tungsten carbide coatings, particularly those applied using the HVOF process and equipment, provide substantial benefits in terms of durability and performance. CNCLATHING is expertise in delivering high-quality tungsten carbide surface finish for your projects requiring superior wear and corrosion protection.

Why Choose Junying for HVOF Tungsten Carbide Coating
–Advanced Technology and Equipment: specialized finishing equipment that handles tungsten carbide with accurate dimensions and superior surface quality.
–Customization Capabilities: customize features according to your requirements, such as unique surface roughness, specific tolerances, and aesthetic appearance.
–Quality Assurance: a comprehensive set of inspection equipment and adheres to rigorous quality control procedures throughout the machining and finishing processes.
–Rapid Turnaround Times: An efficient schedule and skilled workforce enable us to complete projects swiftly and deliver quick turnaround times without compromising on quality.
–Competitive Price: affordable cost for tungsten carbide surface finishing services, help you to balance costs with worthwhile products and services.
–Customer-Centric Service: Responsive communication and support will be provided from the initial quote to the delivery of the finished product.
What Is Tungsten Carbide Coating?
Tungsten carbide coating is a type of thermal spray coating that involves the deposition of a thin metallic layer of tungsten carbide, a compound of tungsten and carbon, onto the surface of a substrate. This coating is applied primarily to improve the wear resistance and hardness of the surface.
Properties of Tungsten Carbide Coating
– Superior hardness exceeds 70 HRC
– High thermal conductivity
– Low thermal expansion
– Excellent resistance to abrasion, erosion and corrosion

What Is HVOF Tungsten Carbide Coating?
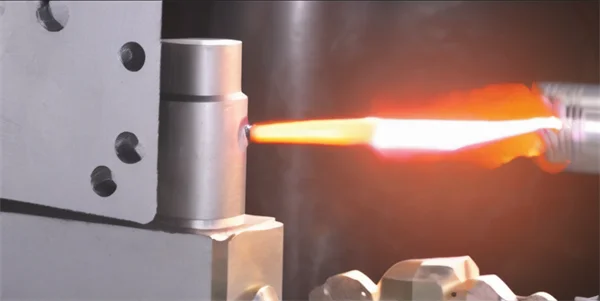
High-velocity oxygen Fuel (HVOF) coating is a thermal spray process used to apply tungsten carbide coatings. In HVOF, a mixture of tungsten carbide powder and a binder material is fed into a high-velocity jet of ignited fuel and oxygen, producing a flame that melts the powder and propels it onto the substrate. The result is a dense, highly adhesive coating layer.

Advantages of HVOF Tungsten Carbide Coating
– High Density and Bond Strength: Exceptionally dense coatings and excellent bond strength with the substrate.
– Low Oxidation: The rapid cooling in the HVOF process minimizes oxidation, resulting in purer and stronger coatings.
– Smooth Surface Finish: A smoother finish compared to other thermal spray processes, reducing the need for post-coating finishing.
– Versatility: It can be applied to a variety of substrates including metals, alloys, and ceramics.
Thickness of HVOF Tungsten Carbide Coating
How thick should be for the HVOF coating? substrate hardness, thermal expansion mismatch, component dimensions, stress concentration points and some other factors would affect the optimal thickness.
– Minimum thickness: generally, a minimum of 0.003-0.005 inches (0.076-0.127 mm) for HVOF WC coatings. The coating thinner than 0.003 inches may be too thin to provide adequate abrasion/impact resistance.
– Maximum thickness: There is no definite maximum, but around 0.08-0.125 inches (2-3 mm) is commonly cited as the practical upper limit due to stresses induced at greater thicknesses.
– Optimal range: For balanced wear protection and minimal cracking/delamination risk, most manufacturers specify 0.008-0.050 inches (0.2-1.3 mm) as the ideal thickness range for HVOF tungsten carbide coatings.
Thinner tungsten carbide coats (<0.008 inches) are suitable for corrosion/erosion protection while thicker ones (>0.050 inches) provide maximum abrasion resistance.
Process of Tungsten Carbide Coating – How Is Tungsten Carbide Coating Done?
High Velocity Oxy-Fuel thermal spraying process uses both fuel and oxygen to combust and accelerate fine tungsten carbide particles to extremely high velocities towards the material or part to be treated.
1. Surface Preparation: The substrate surface is cleaned and roughened to enhance coating adhesion.
2. Coating Application: The tungsten carbide powder is sprayed onto the substrate using the HVOF equipment.
3. Cooling & Solidification: The coated component is allowed to cool, forming a strong mechanical bond.
4. Finishing: The coating may be ground or polished to achieve the desired surface finish.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide Coatings
– Automotive: In engine components and wear parts where durability is crucial.
– Oil and Gas: In drilling and extraction equipment.
– Mining: On drilling heads and excavation tools.
– Metalworking: Dies, injection molding tools, and more that need to extend life.
– Construction: Concrete mixers, demolition shears, bulldozer components, etc.
– Food: Meat saws, slicers, mixers that require non-reactive, non-stick properties.
– Firearms: Rifle barrels and other gun parts.
Tungsten Carbide Coating vs Chromium Carbide Coating, What Are the Differences
– Hardness: Tungsten carbide coatings generally offer greater hardness compared to chromium carbide.
– Temperature Resistance: Tungsten carbide maintains its hardness at higher temperatures than chromium carbide.
– Corrosion Resistance: Chromium carbide coating exhibits better corrosion resistance, especially in acidic and saltwater environments.
– Abrasion Resistance: Tungsten carbide coating has superior resistance to abrasive and erosive wear due to its greater hardness.
– Adhesion: Chromium carbide coating typically bonds better to substrate materials like steel. Tungsten carbide often requires an intermediate nickel bonding layer.
– Cost: Chromium carbide coating has a lower overall cost due to cheaper raw materials and processing requirements compared to tungsten carbide.
– Application: Tungsten carbide is preferable for applications involving higher impact and abrasion. Chromium carbide is often used where oxidation resistance at high temperatures is more crucial.

